Intelligent User Interfaces Home >>>research>>>SeAN: a Server for Adaptive News
SeAN: a Server for Adaptive NewsSeAN is a Web-based system for the provision of personalized news. The project moved from the experience of SETA project and lasted from January 1999 until December 2000. The idea was that of using the same architecture for developing other adaptive systems. Among the customized services, the personalized provision of news holds an important part. This is the reason for developing an adaptive news server. The personalized provision of news, is, in fact, an interesting opportunity for all companies operating on the web, not only for those in the communication field (such as newspapers, radio or television companies). Almost all portals provide access to news and also many companies provide specialized news services, usually related to their commercial fields or to the interests of their customers. The primary goal of these services is to attract web surfers and gaining their loyalty. SeAN is a multi-agent system which can be accessed using any web browser; it aims at personalizing both the selection of topics that are of interest to the user and the detail level of the presentation of each news item. This combination of goals makes SeAN different from other approaches in the literature. In fact, most of the approaches in the literature assume that the repository of news is not structured, i.e., that each news item is a text file (or a set of text files). This makes the administration of the repository very simple and flexible but makes it difficult to define strategies for personalizing the presentation of a document.
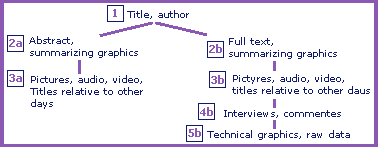
On the other hand, SeAN aims at structuring news in such a way that different detail levels for the presentation of a news item can be obtained dynamically depending on the content of the user model. The original idea of the project is that of considering each news as a chunk of information, namely a complex composite entities, having several attributes that define its components. Examples of attributes (some of them are optional or multi-value) are the title and subtitle of the news, the author(s), an abstract, the text, a set of graphics summarizing the content of the text, photos, video, audio clips; commentaries, interviews, agency reports; raw data and/or detailed charts/graphics, and so forth. These attributes can be aggregated in various ways to define different presentation formats, corresponding to different detail's levels. The aggregations we used are shown in the figure, where a node of the tree corresponds to a presentation format that adds the attributes in the nodes to those inherited from its ancestors. The structured approach adopted for the system conveys some benefits that can be summarized as follows:
Besides the personalization of topics and detail level of news, the system implements also some components for the adaptation of advertisements. User modeling takes into account different dimensions of users (interests, expertise, receptivity, life style) in order to perform the different forms of personalization mentioned above. In particular, stereotypes are used to initialize the user model, while user modeling rules based on the events captured during the navigation are exploited to revise and refine the user model. For more information about this project, please contact
|